Background:
Since its first use from approximately 19th October 2016, TrickBot has frequently issued new versions of its XML configuration file, mcconf. Originally there was a single chain of config versions which started at 1000002. (There may have been a 1000001 but it is not been shared publicly.) I refer to this original sequence as iteration A. On 16th November 2017 TrickBot mcconfs were issued for older version numbers than the current iteration A configs, but with different command and control (C2) servers to those in that version's iteration A config. This indicated the start of iteration B, a new sequence of configs believed to be for a second botnet. While there is a small amount of overlap of the C2 servers between iteration A and iteration B, the majority of C2 servers are specific to an iteration (hence botnet). The iteration B botnet stopped receiving new configs on 28th February 2018. As of 28th March 2018 another iteration, iteration C, was started, once again repeating previously used version numbers but with different C2 server lists. Victim hosts in that third botnet were merged into the iteration A botnet as of 23rd May 2018.
This week's analysis:
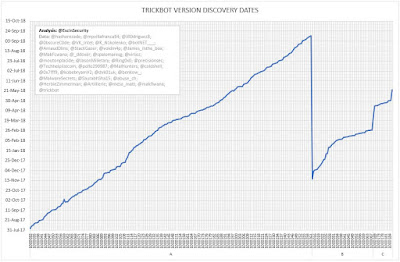
Figure 1 shows the rate of discovery of TrickBot versions in the wild, based on shared mcconfs. The flatter the line, the more frequently versions are discovered. Ignore the two long, almost vertical lines which coincide with the switch from one iteration to the next. These vertical lines are purely an artefact of graphing the data in a single series. (Note: Full size versions of all the graphs and tables are available via the link at the end of this post.)
There were four new config versions discovered in the week commencing 10th September 2018, (A-1000258, A-1000259, A-1000260, and A-1000261), four the week before, and three the week before that. All new config versions extend the iteration A botnet, taking this to 1000261. The secondary, iteration B, botnet was not extended in the discovered versions and remains unchanged since 1000068 of 28th February 2018. The tertiary, iteration C, botnet was merged into the iteration A botnet on 23rd May 2018.
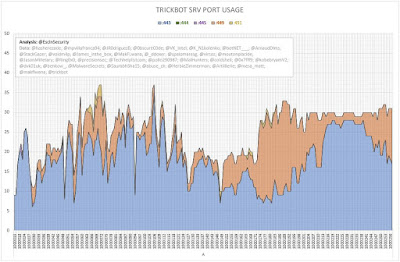
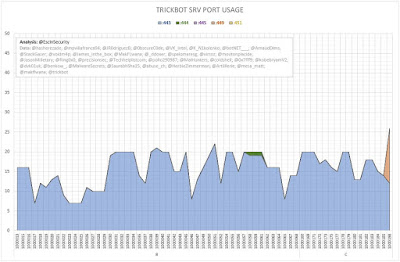
The following graphs (Figures 2 and 3) show the number of server entries using ports:
- 443 (HTTPS);
- 444 (Simple Network Paging Protocol) -- INACTIVE;
- 445 (IBM AS Server Mapper) -- INACTIVE;
- 449 (Cray Network Semaphore Server); and
- 451 (SMB) -- INACTIVE.
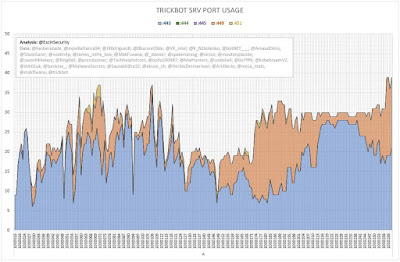 |
| Figure 2 - TrickBot SRV Port Usage (Iteration A) |
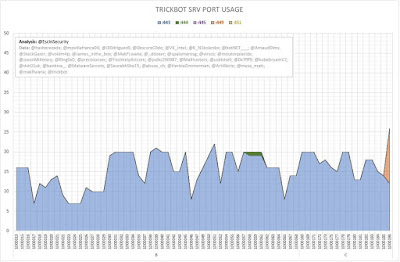 |
| Figure 3 - TrickBot SRV Port Usage (Iterations B and C) |
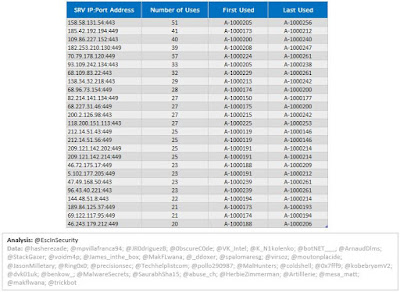 |
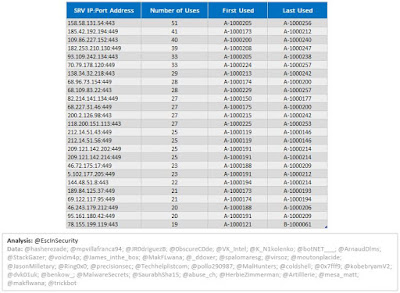
| Figure 4 - TrickBot Top 25 SRV |
The reduced churn percentage, regular number of unique C2 servers used per week, stabilised length of mcconf server list, and stable percentage of :443 servers through the last few months all demonstrate the increased maturity and stability of TrickBot infrastructure management.
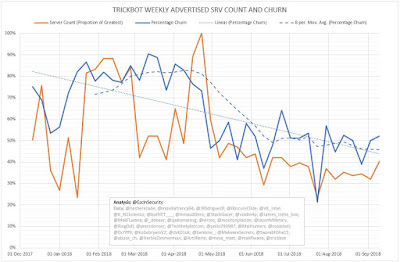 |
| Figure 6 - TrickBot Weekly Advertised SRV Count and Churn |
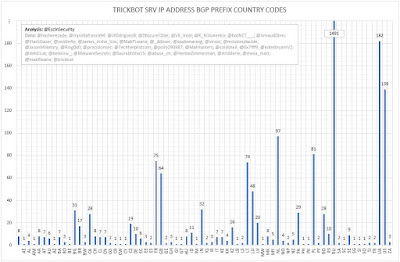 |
| Figure 7 - TrickBot SRV IP Address BGP Prefix Country Codes |
Figure 8 shows the geographical location of 46 (those with location data) of 46 (scanned by Shodan) of the 48 C2 server IP addresses used in the analysed configs.
According to Shodan's most recent data:
According to Shodan's most recent data:
- 19 are MikroTik devices and six are Ubiquiti devices.
- 16 are running OpenSSH, 11 are running nginx, seven are running Apache, five are running Dropbear SSH, three are running Postfix, two are running Exim, one is running Pure FTP. and one is running a Conan Exiles server.
 |
| Figure 8 - TrickBot C2 Server IP Locations For New Configs |
Figure 9 shows the top 25 BGP prefixes used by TrickBot for C2 servers.
Full size versions of the figures included in this post are available here. I also have a page documenting the various discrepancies identified in TrickBot's mcconf files.
Thanks to hasherezade, mpvillafranca94, JR0driguezB, 0bscureC0de, VK_Intel, K_N1kolenko, botNET___, ArnaudDlms, StackGazer, voidm4p, James_inthe_box, MakFLwana, _ddoxer, spalomaresg, virsoz, moutonplacide, JasonMilletary, Ring0x0, precisionsec, Techhelplistcom, pollo290987, MalHunters, coldshell, 0x7fff9, kobebryamV2, dvk01uk, benkow_, MalwareSecrets, SaurabhSha15, abuse_ch, HerbieZimmerman, Artilllerie, and mesa_matt.
This post was made by @EscInSecurity and first appeared on https://escinsecurity.blogspot.com/.
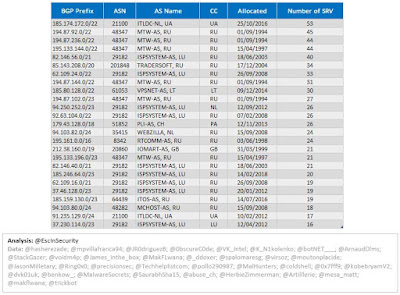 |
| Figure 9 - TrickBot Top 25 BGP Prefixes |
Thanks to hasherezade, mpvillafranca94, JR0driguezB, 0bscureC0de, VK_Intel, K_N1kolenko, botNET___, ArnaudDlms, StackGazer, voidm4p, James_inthe_box, MakFLwana, _ddoxer, spalomaresg, virsoz, moutonplacide, JasonMilletary, Ring0x0, precisionsec, Techhelplistcom, pollo290987, MalHunters, coldshell, 0x7fff9, kobebryamV2, dvk01uk, benkow_, MalwareSecrets, SaurabhSha15, abuse_ch, HerbieZimmerman, Artilllerie, and mesa_matt.
This post was made by @EscInSecurity and first appeared on https://escinsecurity.blogspot.com/.