Since its first use in approximately October 2016, TrickBot has frequently issued new versions of its XML configuration file, mcconf. Originally there was a single chain of config versions which started at 1000002. (There may have been a 1000001 but it is not been shared publicly.) I refer to this original sequence as iteration A. In November 2017 TrickBot mcconfs were issued for older version numbers than the current iteration A configs, but with different command and control (C2) servers to those in that version's iteration A config. This indicated the start of iteration B, a new sequence of configs believed to be for a second botnet. While there is some overlap of the C2 servers between iteration A and iteration B, the majority of C2 servers are specific to an iteration (hence botnet). As of late March 2018 another iteration, iteration C, was started, once again repeating previously used version numbers but with different C2 server lists.
The following graph shows the rate of discovery of TrickBot versions in the wild, based on shared mcconfs. The flatter the line, the more frequently versions are discovered. Ignore the long almost vertical lines which coincide with the switch from one iteration to the next. These vertical lines are purely an artefact of graphing the data in a single series. (Note: Full size versions of all the graphs and tables are available via the link at the end of this post.)
There were three new config versions discovered in the week commencing 7th May 2018 (A-1000190, A-1000191, and A-1000192), six the week before, and 11 the week before that. All of the three new config versions extend the iteration A botnet, taking this to 1000192. The secondary, iteration B, botnet was not extended in the discovered versions and remains unchanged since 1000068 of 28th February 2018. The tertiary, iteration C, botnet was also not extended in the discovered versions and remains unchanged since the previous week at 1000185.
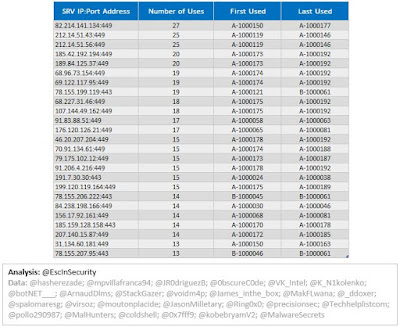
The following graph shows the number of server entries using ports:
- 443 (HTTPS);
- 444 (Simple Network Paging Protocol) -- INACTIVE;
- 445 (IBM AS Server Mapper) -- INACTIVE;
- 449 (Cray Network Semaphore Server); and
- 451 (SMB) -- INACTIVE.
The following map shows the geographical location of 44 (those with location data) of 44 (scanned by Shodan) of the 50 C2 server IP addresses used in the analysed configs.
According to Shodan's most recent data:
The following table shows the BGP allocations of C2 servers' IP addresses to country by TrickBot version. (Once again, I know it's unreadable - it's just here as a guide to show what's in the downloadable zip file at the bottom of the post.)
According to Shodan's most recent data:
- 14 are Ubiquiti devices.
- 21 are running Dropbear SSH, 14 are running OpenSSH, seven are running nginx, five are running Apache, three are running Exim, two are running Postfix, and one is running ProFTP.
Finally, the following table shows the top 25 BGP prefixes used by TrickBot for C2 servers.
Full size versions of the images included in this post are available here. I've also created a page documenting the various discrepancies identified in TrickBot's mcconf files.
Thanks to @hasherezade, @mpvillafranca94, @JR0driguezB, @0bscureC0de, @virsoz, @spalomaresg, @VK_Intel, @K_N1kolenko, @botNET___, @ArnaudDlms, @StackGazer,@voidm4p, @James_inthe_box, @MakFLwana, @_ddoxer, @moutonplacide, @JasonMilletary,@Ring0x0, @precisionsec, @Techhelplistcom, @pollo290987, @MalHunters, @coldshell, @0x7fff9, @kobebryamV2, and @MalwareSecrets for sharing the mcconfs.
Thanks to @hasherezade, @mpvillafranca94, @JR0driguezB, @0bscureC0de, @virsoz, @spalomaresg, @VK_Intel, @K_N1kolenko, @botNET___, @ArnaudDlms, @StackGazer,@voidm4p, @James_inthe_box, @MakFLwana, @_ddoxer, @moutonplacide, @JasonMilletary,@Ring0x0, @precisionsec, @Techhelplistcom, @pollo290987, @MalHunters, @coldshell, @0x7fff9, @kobebryamV2, and @MalwareSecrets for sharing the mcconfs.